Evaluating patients’ individual response regarding anti-inflammatory preparations using the TNF-α inhibitor test
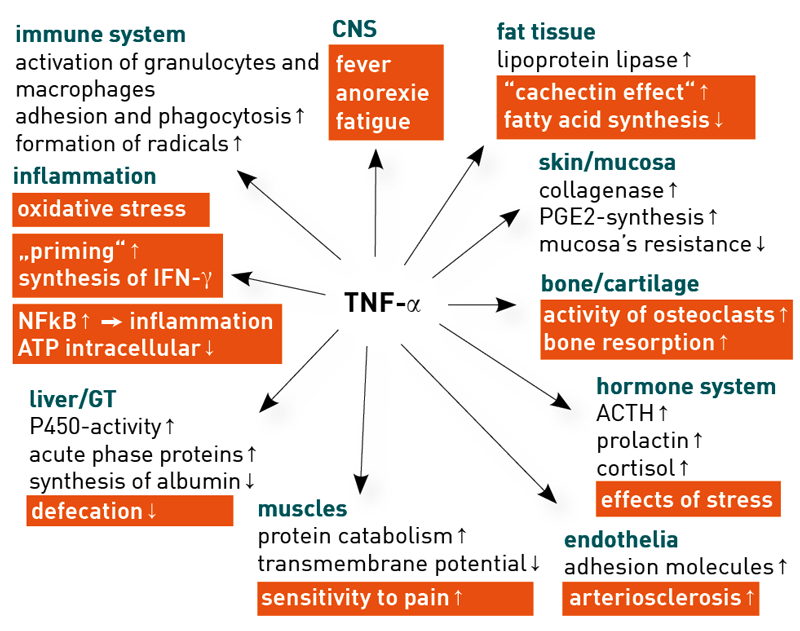
TNF-α as a pro-inflammatory key cytokine
Tumour necrosis factor alpha (short: TNF-α) is a cytokine, which is involved in almost all inflammatory reactions. TNF-α is the first cytokine to be expressed in activated macrophages’ signalling cascade. Its most important function is the activation of various immune cells. TNF-α has the ability to promote cell differentiation and the expression of other cytokines. Within the CNS, it causes fever, fatigue, gene-ral feeling of illness and affects the lipid meta-bolism, blood coagulation, insulin resistance, and the convalescence of patients with arteriosclerosis.
In rheumatology, TNF-α blockers are administered as longterm anti-rheumatic drugs. Remicade®, Humira® and Enbrel® are antibody preparations that block TNF-α’s effect at its receptors on target cells. The preparations above do not inhibit the expression of TNF-α by macrophages. For this therapy approach only the typical anti-inflammatory preparations (e.g. prednisolone) as well as numerous phytopharmaceuticals and some dietary supplements with described anti-inflammatory properties are available so far.
However, regarding their clinical activity, patients show varying responses, which is due to highly differing and individual numbers of toll-like receptors on macrophages.
Therefore, running the TNF-α inhibitor test as a pretest is sensible, if the most effective preparation for an adjuvant anti-inflammatory therapy in an individual case needs to be pre-selected.
Principle of the test
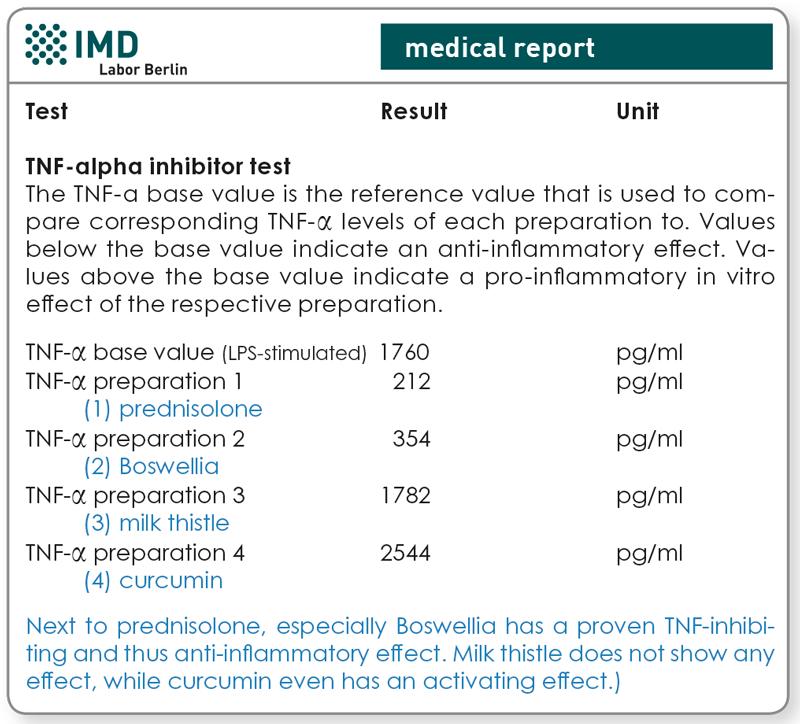
The standardised expression of LPS-induced TNF-α (TNF-α base value) is used as a reference value. In replicate controls, the LPS-induced TNF-α secretion is analysed under the influence of added preparations.
Note: LPS (lipopolysaccharide) is a surface molecule of gram-negative bacteria, which induces a significant inflammatory response (TNF-α secretion) in monocytes/macrophages by binding to their CD14 molecules
Is the test sensible only in cases with increased TNF-α levels in blood?
No, TNF-α is used only as a marker cytokine for the activation of macrophages. By detecting the release of TNF-α, the test assesses whether the respective preparation has an impact on the inflammatory cascade. Regarding the detection of LPS-induced inflammatory responses, TNF-α has proven a more sensitive and better test than IL-1 or IL-6. Therefore, the TNF inhibitor test is beneficial in context with any type of myelomonocytic inflammation, even if it has been proven only via increased CRP, IL-1, or IL-6. The TNF-α inhibitor test is a global inflammation inhibitor test.
Material
10 ml heparin blood
Sample receipt within 24 hours must be assured. The blood sample is to be stored and transported at room temperature. Within the Berlin city area, we offer a courier service (+49 (0)30 7701-250). For collections beyond Berlin, please contact our free of charge courier service +49 (0)30 77001-450
Costs
Please obtain the costs for the analysis from the pdf-document.
These preparations are established for the TNF-alpha inhibitor test and are available in the laboratory (alphabetic order).
In case you would like to test a preparation that is not listed above, we would kindly ask you to add it to your sample when sending it to us. Upon request, the preparation can be stored up to 3 months in the laboratory to assure substance stability for further tests (please indicate on the transfer form).
Regarding “TNF-alpha blockers” such as Enbrel® (Etanercept), Remicade® (Infliximab) or Humira® (Adalimumab), the TNF inhibitor test is not useful, since the effect of these substances is not based on a reduced release of TNF-α from monocytes/macrophages. Those three substances block TNF-α effect in the blood or at the target cell.
